Since the inception of Bitcoin, the underlying blockchain technology has come far. With increasing needs for scalability have emerged innovative solutions to get blockchains to do more in less time. Sharding is a solution for this heightened scalability, in a very brief answer to our titular question- ‘what is sharding?’
Sharding in blockchain basically allows you to break a bigger database into smaller parts, so work can be delegated to these minions at peak hours and the overall output is increased by much. How sharding works, and what are the advantages and disadvantages of sharding, you wonder? Let’s find out all about that!
What is Sharding?
Starting with a proper definition- what is sharding? When you divide a larger blockchain into smaller parts, these parts are called shards, which can be stored on separate servers.
Simply put, large data sets are divided into small chunks that can be processed by separate servers.
Features of sharding? Here’s what the technique generally encompasses:
- Sharding helps improve a database system’s performance, scalability, and stability.
- Instead of having a single, extensive database that can become overloaded, sharding distributes the data and workload among multiple smaller databases, allowing for more efficient and effective processing.
- By sharding, along with the risk of data overload, downtime is also reduced and the system can handle an increased volume of requests and data in lesser time.
How Does Sharding Work?
Now we know the answer to ‘what is sharding?’, but how sharding works? Let’s find that out next:
- A bigger database is divided into several shards to delegate the workload.
- Each shard is stored on a separate server and can be accessed and managed independently.
- When a user requests information from the database, the system directs the request to the specific shard that holds the data.
- The technique improves performance of databases like blockchains by reducing the amount of data each server must manage, and it allows the system to scale by adding more servers as the sharding database grows.
Sharding is a solution to scaling a database to handle growing amounts of data and traffic. It enables unlimited scaling by providing enhanced read/write speed, ample storage, and high availability. This way, sharded databases can handle the increased load without any disruption.
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) and Sharding
Now, let’s understand how sharding works in distributed ledger technology, like blockchains:
Distributed ledger technology involves the implementation of protocols and infrastructure that enable computers located in various locations to efficiently suggest and validate transactions, and keep records updated across a network in a coordinated manner.
In distributed ledger technology like blockchains, once the data is recorded, it forms an immutable database that is governed by the rules of the network. Now, in the context of blockchains, this technique offers a viable solution to the scalability challenges faced.
- Sharding in distributed ledger technology allows nodes to validate and store just a subset of all the messages the network exchanges.
- This reduces and distributes the load of the data to be processed, so the network’s capability increases as compared to a non-sharded solution.
- By dividing the blockchain into smaller, interconnected pieces, the technique can boost transactions throughout and reduce congestion.
Scalability and Sharding
Sometimes blockchain networks might struggle with increased transaction volumes, which can lead to slow confirmation times and high fees. How sharding works to address this issue is by enabling multiple shards to process transactions concurrently, significantly increasing the network’s capacity. Let’s understand more on this:
- Sharding databases enhances the horizontal scalability of blockchain networks. Horizontal scalability refers to the capability of expanding the system’s capacity by incorporating additional nodes into the network, as opposed to improving the performance of individual nodes to process more transactions in blockchain.
- Through this system, transactions are split into smaller fragments, which are then processed simultaneously by different shards.
- Sharding database results in the ability to handle a higher volume of transactions at once, thus enhancing the scalability of the network as a whole.
How is Sharding Done?
The implementation varies depending on the specific blockchain or database system. As now we understand the concept of how sharding works, let’s understand this process of implementation.
- First, a database is designed to store data in various sets, consisting of columns and rows.
- Sharding database divides a single set into smaller segments, known as shards. Each shard comprises distinct rows of information that can be stored on different computers, referred to as nodes.
- Although the shards are stored on separate nodes, they all follow the same schema or structure as the original database.
- The data that has been divided is referred to as logical shards, and the machine that holds these logical shards is known as a physical shard or database node.
- A single physical shard may store multiple logical shards.
- Developers use a shard key to decide how to divide the dataset in a sharding database. In addition, developers can incorporate code into their applications to store or retrieve data from the appropriate physical shard or shards.
For instance, a database without this technique that holds data for customer records might appear like this.
| Customer ID | Name | State |
| 1 | Ray | India |
| 2 | Jasmin | USA |
| 3 | Paul | Europe |
| 4 | Chan | China |
The technique involves dividing the rows of information from the table and storing them on separate machines, as depicted below.
Computer A
| 1 | Ray | India |
| 2 | Jasmin | USA |
Computer B
| 3 | Paul | Europe |
| 4 | Chan | China |
Shard Sharing
Shard sharing involves the partitioning of a big database into smaller components referred to as shards. These shards are then stored on different machines, thereby increasing the efficiency and scalability of the sharding database. This technique is widely utilized in the field of blockchain to boost the network’s speed and stability.
Advantages of Sharding
There are several advantages of this method, which makes it an attractive solution for improving the scalability and performance of blockchain and distributed database systems.
- Scalability: The primary benefit of this method is its ability to scale a network horizontally. As transaction volumes increase, more shards can be added, allowing the network to handle a growing number of transactions efficiently.
- Improved Throughput: Sharding enhances transaction throughput by enabling multiple shards to process transactions simultaneously. This results in faster confirmation times and reduced congestion.
- Lower Transaction Costs: With increased throughput and reduced congestion, transaction fees on sharded networks tend to be lower, making it more cost-effective for users.
- Enhanced Security: This technique maintains the security and decentralization of blockchain networks. How sharding works is that each shard operates independently, reducing the impact of potential attacks on the entire network.
- Better Resource Utilization: One of the advantages of this method is better resource utilization. The method optimizes resources by distributing the workload evenly across nodes, preventing bottlenecks and resource wastage.
Disadvantages of Sharding
While there are significant advantages of sharding, it is essential to consider potential disadvantages of sharding as well.
- Complex Implementation: Implementing sharding databases can be technically challenging, requiring careful planning, design, and coordination. Ensuring proper communication and coordination between shards is crucial and may introduce complexities.
- Data Fragmentation: Data fragmentation across shards can make it challenging to access and query data that spans multiple shards.
- Network Upgrades: Implementing this technique may require significant network upgrades, which can disrupt the existing ecosystem.
- Initial Centralization: Some sharding implementations may involve a degree of centralization during the early stages of shard creation. This is because the network needs to ensure that each shard has a sufficient number of nodes and that nodes are evenly distributed.
- Interoperability: Ensuring interoperability between different sharded networks and legacy systems can be complex. Interoperability is about enabling different sharded networks or blockchains to communicate and interact with each other.
Now, despite the disadvantages of sharding, it’s important to keep in mind that any technology has its drawbacks that can be improved upon with time and effort. Sharding for blockchains is a wonderful solution to end scalability issues, and in the near future, the aforementioned shortcomings can be accordingly dealt with to improve sharding databases.
Applications and Platforms
Several blockchain platforms use this method to improve scalability and performance. However, sharding can be complex and requires significant network upgrades. Despite these challenges, these platforms are making continuous efforts to enhance their systems and provide better services to their users.
NEAR Sharding
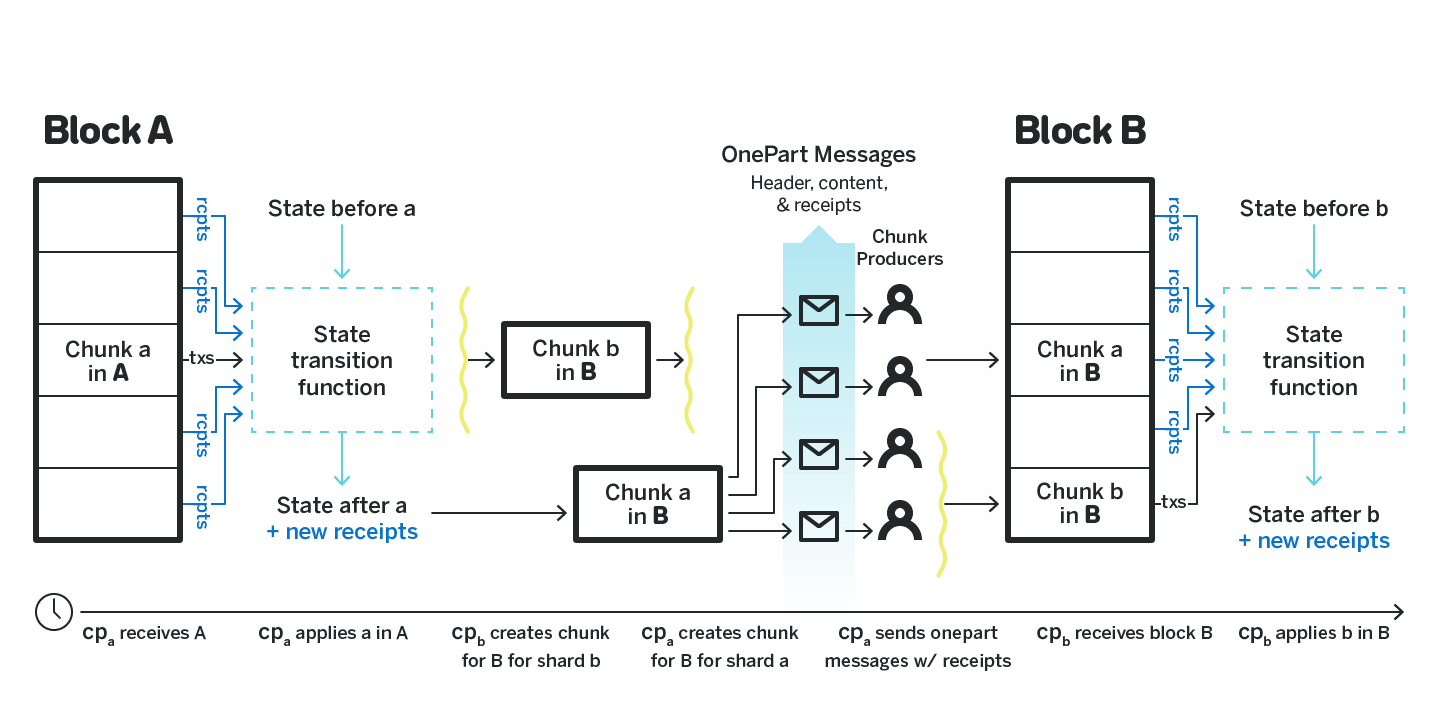
NEAR is a decentralized platform that uses sharding to improve performance and scalability. Sharding is the division of a large database into smaller parts called “shards”, each stored and processed on a separate node.
NEAR implements sharding to enhance the execution of smart contracts and decentralized applications. This allows for parallel processing and increased transaction throughput, making the platform more efficient and able to handle growing user demand.
NEAR aims to provide an easy-to-use platform for building and deploying applications, with a focus on usability and developer experience.
The objective of sharding the network is to enhance its performance and scalability by dividing it into smaller parts, known as “shards”. This allows for parallel processing and increased transaction throughput, making the platform more efficient and capable of handling a growing user base.
NEAR’s focus is on providing an accessible platform for building and deploying applications, with a strong emphasis on user experience and developer ease.
Ethereum Beacon Chain

The Ethereum Beacon Chain is a key component of Ethereum 2.0, which is a long-planned upgrade to the Ethereum network. The Beacon Chain is a proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchain that serves as the central coordination and management layer for Ethereum 2.0.
Sharding is a crucial aspect of Ethereum 2.0. It divides the Ethereum network into smaller units, called “shards”, which can process transactions and run smart contracts in parallel. This improves overall performance by increasing transaction processing capacity, reducing congestion, and providing a more efficient system.
Sharding enhances Ethereum’s ability to support a larger number of transactions and decentralized applications, enabling it to scale to meet growing user demand.
Polkadot Parachain

A Parachain in the Polkadot network is a separate blockchain that operates alongside the main network. The Polkadot network is built to support multiple blockchains and allow them to communicate with each other seamlessly.
Parachains allow for these separate blockchains to connect to the Polkadot network and participate in consensus as equal peers, while still maintaining their own independent state and consensus mechanism. This enhances scalability, reduces congestion, and allows different blockchains to share resources and services.
Sharding is not a concept specifically tied to the Polkadot Parachains. However, the Polkadot network as a whole uses sharding in its design to increase scalability and improve the overall performance of the network.
Sharding in the context of Polkadot refers to the division of the network into multiple shards, each of which can process transactions and validate blocks in parallel. This allows for increased transaction processing capacity and reduced congestion, making the network more efficient and capable of supporting a larger number of users.
The use of sharding in the design of the Polkadot network helps to ensure that it can scale to meet the demands of a growing user base and support a wider range of decentralized applications.
The Road Ahead
We hope this post has answered ‘what is sharding?’ to your satisfaction! As you may have gathered by now, sharding databases is a powerful technique that holds the potential to reshape the future of blockchain technology. Its ability to address scalability challenges while maintaining security and decentralization makes it a promising solution for a wide range of applications.
As the technology evolves, we can expect to see more sharded networks powering the next generation of decentralized applications and services, unlocking new possibilities in the digital landscape. Embracing the advantages of sharding while addressing its challenges will be crucial for the successful adoption of this innovative approach.



